PSMA PET/MRI Accurately Predicts Prostate Cancer Recurrence Risk
 Prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET/MRI can successfully determine whether cancer is likely to return within two years of a prostatectomy in men recently diagnosed with intermediate or high-grade prostate cancer. The research, published in the The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, will help physicians identify patients who could benefit from additional treatment and/or frequent surveillance.
Prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET/MRI can successfully determine whether cancer is likely to return within two years of a prostatectomy in men recently diagnosed with intermediate or high-grade prostate cancer. The research, published in the The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, will help physicians identify patients who could benefit from additional treatment and/or frequent surveillance.
Prostate cancer is known to have very variable behavior and outcomes. While many cases of localized prostate cancer can be treated successfully, some patients experience a rapid progression even after prostatectomy or radiation therapy. Therefore, initial risk stratification is important to determine treatment decisions and subsequent management of prostate cancer patients.
“Clinicians currently use biopsy findings and clinical information, such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, to predict if prostate cancer is slow- growing or if it will spread quickly and require aggressive treatments,” said Andrei Iagaru, MD, professor of Radiology–Nuclear Medicine and chief of the Division of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging at Stanford University Medical Center in Stanford, California. “However, functional imaging, such as PET/MRI, is increasingly being considered as a way to identify patients at risk for persistent or recurrent disease.”
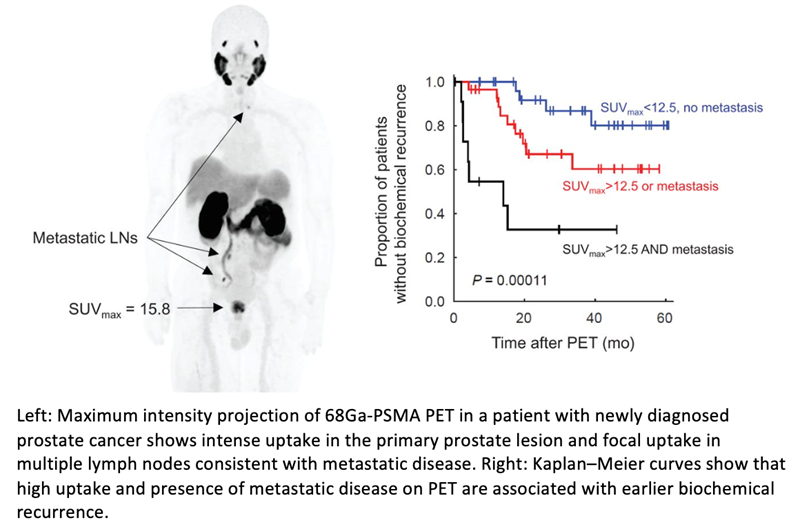
In the study, researchers examined the value of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MRI for risk stratification of newly diagnosed prostate patients prior to initial therapy. Seventy-three patients with a new diagnosis of intermediate- or high-grade prostate cancer were imaged with 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MR between April 2016 and December 2020. PET findings were divided into groups based on low versus high uptake in the primary lesion and the presence or absence of metastatic disease. These findings were compared to biopsy results and clinical information. The relationship between the PET/MRI findings and patient outcomes were also examined.
High uptake in the primary lesion and the presence of PSMA metastasis were associated with biochemical failure or rapid recurrence within two years of prostatectomy. In contrast, patients with low uptake in the primary lesion who did not have evidence of metastatic disease on PET/MRI had a low likelihood of experiencing recurrence during the follow-up period.
“PSMA PET/MRI adds value to the pre-therapy evaluation of patients with newly diagnosed prostate cancer, and the information from PET seems to be as reliable, if not more reliable, than biopsy findings and clinical information in predicting which patients will have suboptimal outcome,” stated Farshad Moradi, MD, PhD, clinical associate professor of Radiology–Nuclear Medicine at Stanford University Medical Center in Stanford, California. “This study provides support for including PSMA PET to aid in clinical decision making about prostate cancer therapy options. PSMA pre-surgery may contribute to establishing one of the ‘killer applications’ for PET/MRI.”