Radiation Therapy-Induced Toxicity in a Breast Cancer Patient With Variance of Unknown Significance in the Ataxia Telangiectasia
Case Summary
A 51-year-old woman presented in 2018 after a screening mammogram discovered asymmetry in the right subareolar region with a 15 × 13 × 14 mm mass on ultrasonography. Breast biopsies revealed triple-positive infiltrating ductal carcinoma. She had no history of collagen vascular diseases or prior radiation. Genetic testing revealed a heterozygous variance of unknown significance (VUS) in the ataxia telangiectasia (
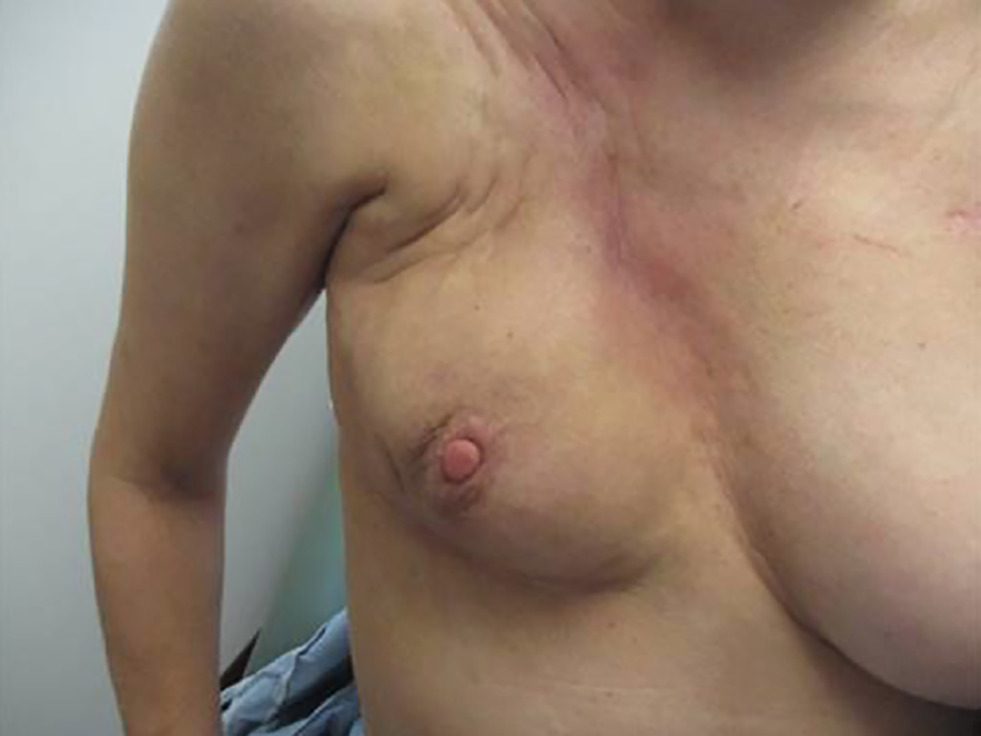
The patient developed cutaneous symptoms, which progressed to telangiectasias and significant fibrosis (
Significant fibrosis and poor cosmesis seen following radiation.
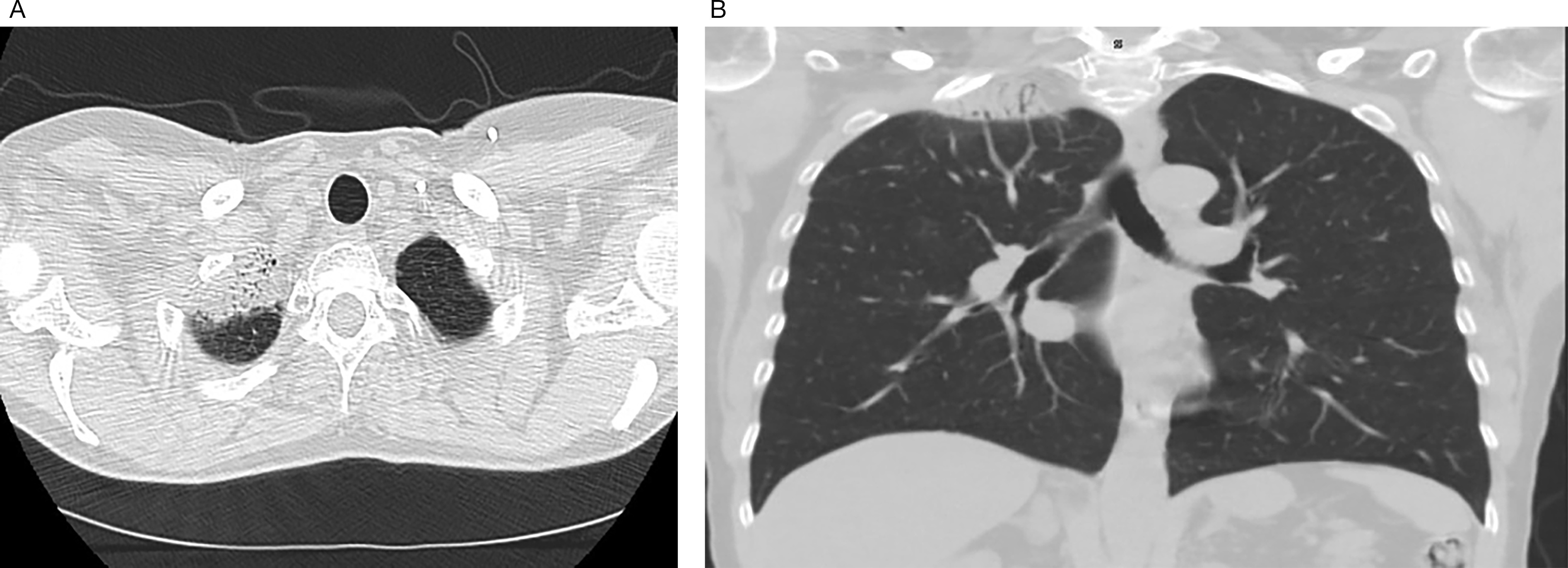
Apical scarring of the right lung following radiation as seen on an axial view (<bold>A</bold>). Apical scarring of the right lung following radiation as seen on a coronal view (B).
Platelet-rich infusions, used for fibrosis treatment, were ineffective. The patient subsequently underwent a mastectomy.
Discussion
By facilitating DNA double-stranded breaks, ionizing radiation is known to cause damage to both malignant and nonmalignant cells. In patients with mutant
Clinical investigations attempting to assess the link between VUS and increased radiation sensitivity have been unclear, with different studies yielding contradictory results. In a study assessing 91 evaluable carriers of
However, one case series demonstrated that patients with heterozygous germline
Conclusions
The
References
- Dosani M, Schrader KA, Nichol A Severe late toxicity after adjuvant breast radiotherapy in a patient with a germline ataxia telangiectasia mutated gene: future treatment decisions. Cureus. 2017; 7(9):undefined-undefined
- Ho AY, Fan G, Atencio DP Possession of ATM sequence variants as predictor for late normal tissue responses in breast cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007; 3(69):677-684
- Hosoya N, Miyagawa K Implications of the germline variants of DNA damage response genes detected by cancer precision medicine for radiological risk communication and cancer therapy decisions. J Radiat Res. 2021; supplement_1(62):i44-i52
- Modlin LA, Flynn J, Zhang Z Tolerability of breast radiotherapy among carriers of ATM germline variants. JCO Precis Oncol. 2021; undefined(5):undefined-undefined
- Pitter KL, Casey DL, Lu YC Pathogenic ATM mutations in cancer and a genetic basis for radiotherapeutic efficacy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021; 3(113):266-273
- Mullins BT, Gupta G Increased radiation toxicity with germline ATM variant of uncertain clinical significance. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2019; 6(24):672-680
- Reiner AS, Robson ME, Mellemkjær L Radiation treatment, ATM, BRCA1/2, and CHEK2*1100delC pathogenic variants and risk of contralateral breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2020; 12(112):1275-1279
- Bergom C, West CM, Higginson DS The implications of genetic testing on radiation therapy decisions: a guide for radiation oncologists. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019; 4(105):698-712
- McGuire KP, Mamounas EP Management of hereditary breast cancer: ASCO, ASTRO, and SSO guideline. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020; 6(27):1721-1723
Citation
Desai AN, Nini KT, Desai GR. Radiation Therapy-Induced Toxicity in a Breast Cancer Patient With Variance of Unknown Significance in the Ataxia Telangiectasia Gene. Appl Radiat Oncol. 2023;(3):1-3.
doi:10.37549/ARO-D-23-00015
September 1, 2023