Adding DWI Improves Differentiation of Locally Recurrent Pancreatic Cancer
 A study in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) reports that adding diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) to conventional MRI improves the differentiation of locally recurrent tumor and post-surgical fibrosis after pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) resection, primarily due to improved sensitivity for recurrence.
A study in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) reports that adding diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) to conventional MRI improves the differentiation of locally recurrent tumor and post-surgical fibrosis after pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) resection, primarily due to improved sensitivity for recurrence.
“The findings indicate a potential role for MRI with DWI in surveillance protocols after PDAC resection,” clarified corresponding author Tae Wook Kang, MD from Samsung Medical Center in Seoul, South Korea.
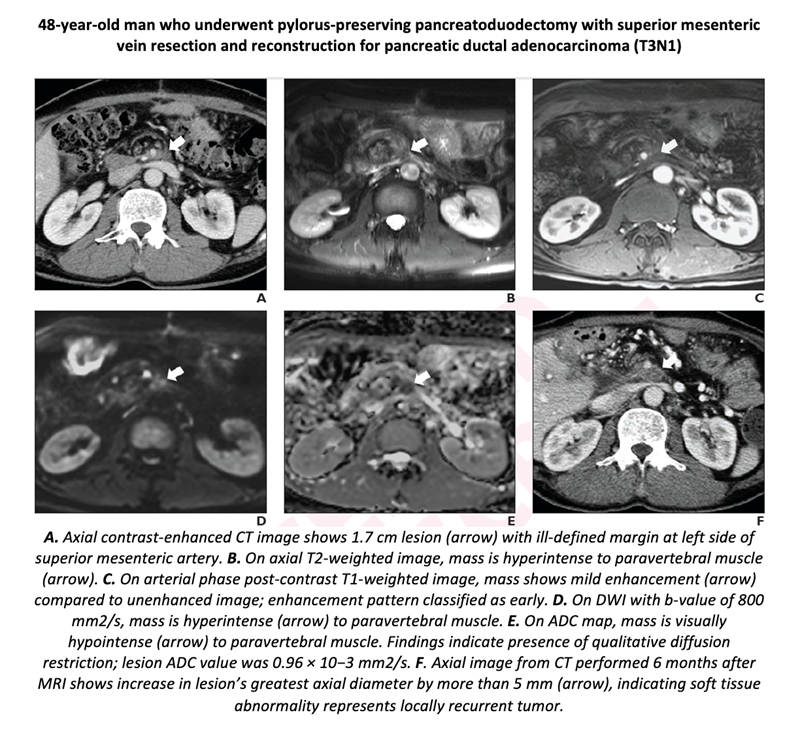
Kang and colleagues’ retrospective study included 66 patients (35 men, 31 women; mean age, 60.5 years) with PDAC resection between January 2009 and March 2016, who underwent postoperative surveillance CT demonstrating a soft tissue lesion at the operative site or at the site of peripancreatic vessels and subsequent MRI with DWI for further evaluation. CT at least 6 months after MRI served as reference standard, with increase in size of the soft tissue by ≥5 mm differentiating locally recurrent tumor (n=26) and post-surgical fibrosis (n=40). Two observers independently reviewed MRI examinations in separate sessions: conventional MRI alone vs MRI with DWI.
Compared with MRI alone, MRI and DWI showed higher sensitivity (observer 1: 88.5% vs 61.5%, p=.008; observer 2: 84.6% vs 42.3%, p= .001) without difference in specificity (observer 1: 72.5% vs 80.0%, p=.08; observer 2, 95.0% vs 85.0%, p=.10) in detecting local recurrence after PDAC resection.
The authors add, “MRI with DWI as a problem-solving tool during post-operative surveillance after PDAC resection could facilitate earlier detection of recurrences, guiding prognostic assessment and treatment decisions.”