Philips’ Spectral 4D CT Radiotherapy Solution Nets FDA Clearance
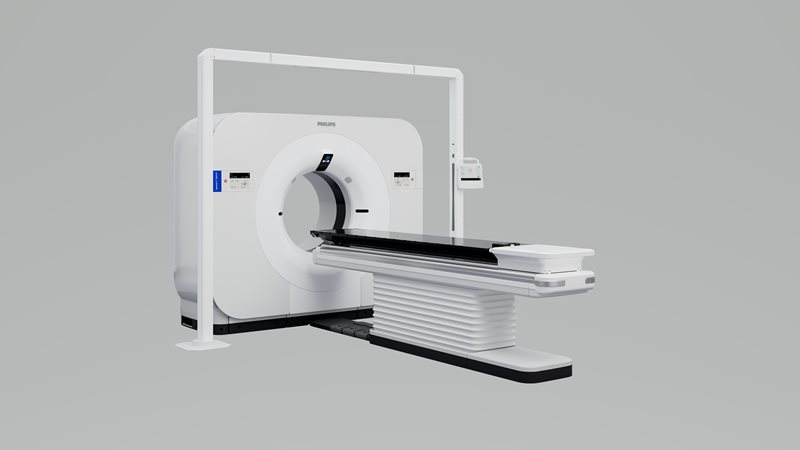 Royal Philips announced US FDA 510(k) clearance for its new detector-based spectral CT radiotherapy solution. Philips Spectral CT 7500 RT marks the next step in personalized cancer care by integrating the unique tumor visualization and tissue characterization capabilities of spectral CT into cancer treatment and planning. Radiation oncologists can now precisely target radiation therapy to the specific physiological characteristics of a patient's tumor, minimizing damage to healthy surrounding tissue and reducing potential unwanted side effects.
Royal Philips announced US FDA 510(k) clearance for its new detector-based spectral CT radiotherapy solution. Philips Spectral CT 7500 RT marks the next step in personalized cancer care by integrating the unique tumor visualization and tissue characterization capabilities of spectral CT into cancer treatment and planning. Radiation oncologists can now precisely target radiation therapy to the specific physiological characteristics of a patient's tumor, minimizing damage to healthy surrounding tissue and reducing potential unwanted side effects.
Spectral CT 7500 RT combines true conventional and spectral CT capabilities in a single scan, seamlessly integrating into existing clinical workflows. As the first radiation therapy CT scanner to offer respiratory-gated spectral imaging, radiation oncologists have all the benefits of 4D conventional CT, and can also now apply the improved visualization and quantification of spectral CT. This latest innovation from Philips benefits radiotherapy departments by reducing the costs of additional scans while enhancing accuracy and enabling more effective treatment plans for a greater number of cancer patients.
“Tumor delineation, beam attenuation, and respiratory motion are critical factors in radiotherapy planning. The spectral information provided by Spectral CT 7500 RT enhances tissue characterization, enabling wider access to highly personalized and precisely targeted treatment for more patients without adding extra steps to current radiotherapy workflows,” said Dan Xu, Global Business Leader of CT at Philips.
Longarino et al demonstrated that spectral CT can reduce proton stopping-power ratio (SPR) error by more than 50% compared to conventional CT, improving the accuracy of radiation treatment and sparing healthy tissue. Philips Spectral CT 7500 RT acquires both true conventional CT and spectral CT information in a single scan. It can automatically create the SPR map and direct electron density (ED) results with less than 1% deviation to enhance both the dose calculation and accuracy of radiotherapy planning.
"The Spectral CT system provides us with several capabilities that conventional CT does not have. It can provide electron density and effective atomic number results, which we can convert to the proton stopping-power ratio. And published data shows that the stopping power ratio obtained in this way has fewer uncertainties compared to regular calibration curves, thereby reducing the uncertainty margins during treatment planning," said Dr. Zhong Su, Physics Director, Department of Radiation Oncology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS) Medical Center (Arkansas, USA).